Schemc
For the majority of manufacturing uses, pure aluminum is too soft. As a result, most aluminum coils are produced and delivered as an alloy. These alloys contain two or more elements, at least one of which is aluminum. The Aluminum Association oversees the four-digit number system to identify aluminum alloys for sheet products. Aluminium's mechanical and other qualities can be adjusted to satisfy particular demands for strength, formability, and other properties when alloyed with other metals.
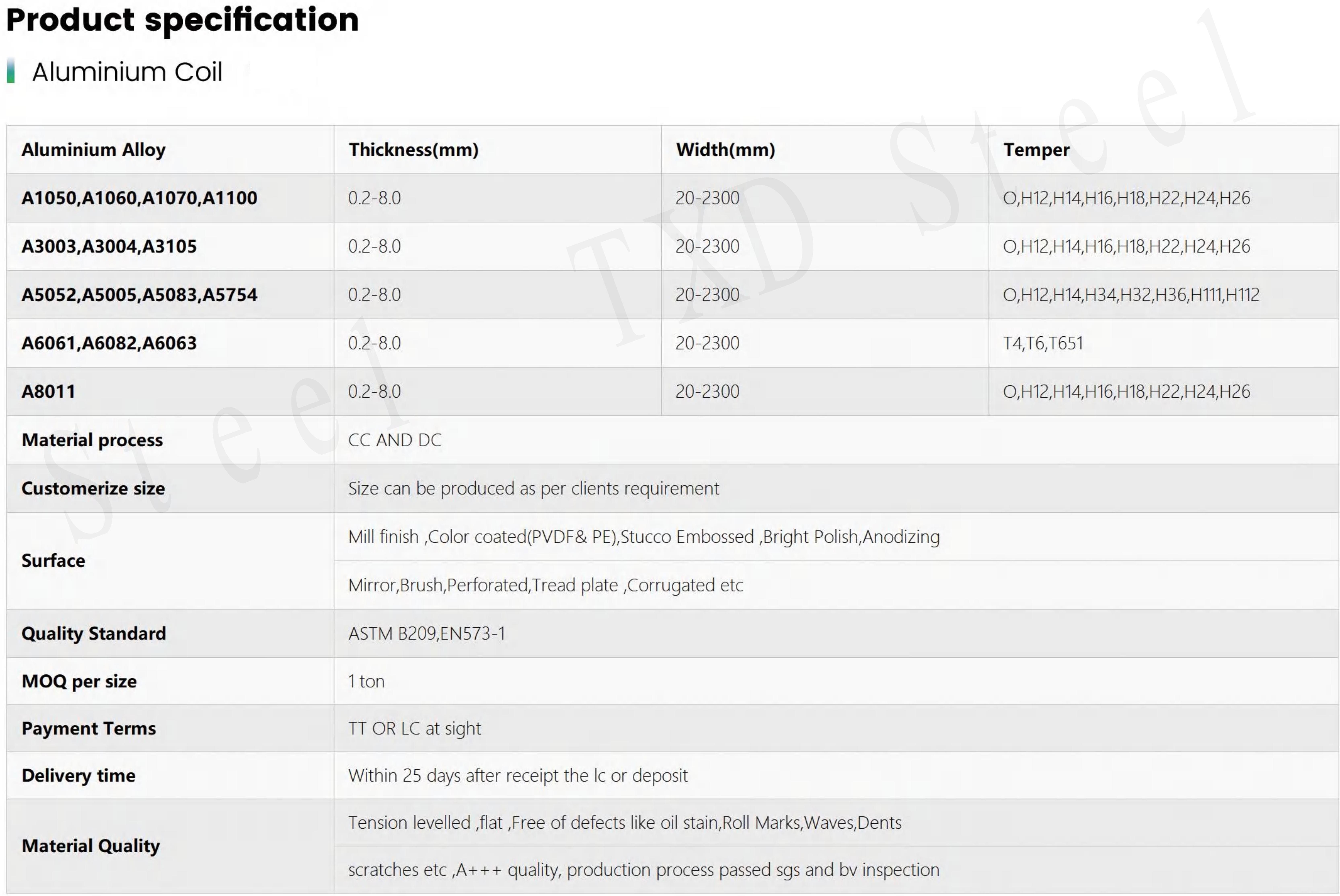
Aluminum coil, often known as "gauge," is offered in different lengths, widths, and thicknesses. The size of the components created and the production technique employed define the precise dimensions. In addition, many surface treatments are available, such as mill, matte, and brilliant. The choice will be based on the intended purpose and appearance of the finished component.
Also available in a variety of tempers is the aluminum coil. "F" temper, which has no set mechanical restrictions and no specific control over the thermal or work-hardening conditions has been applied, may be offered as "manufactured." This method is typically utilized for products in the middle of the production process because it is variable. Another choice pertains to wrought items strengthened by cold-rolling or cold-working, known as strain-hardened. The metal can also be annealed, which means it has to go through a controlled heating process to achieve the ideal balance of strength and formability.
There are numerous uses and industries for the coil. Many stamped and molded components in electronics, medicine, transportation, and other industries use it as their preferred material.
Transportation: It is extensively employed for transportation, as was already indicated. It is utilized in the auto industry to create anything from radiators and wheel hubs to engine parts and automobile doors. Using aluminum to substitute heavier metals can significantly reduce vehicle weight as the automotive industry works to do so. The term "lightweighting" represents optimizing all components to have the lowest weight.
Electronics: Aluminum is used in many industrial and consumer electronics because metal is an excellent conductor of electricity, retains heat, and is corrosion-resistant. Heat sinks, stamped components, shielding, and bigger components, like enclosures, can all be produced using it.
Consumer Goods and Hardware: Packaging for health and beauty products, tools and other hardware, building applications, jewelry, and a huge variety of other common objects all use aluminum parts made from aluminum coil.
Medical: Aluminum is widely used in the medical and dental fields for many products ranging from disposables to surgical equipment and sophisticated electronic devices.
Aerospace: Some aluminum alloys and tempers are perfect for aerospace applications due to their small weight, ability to resist corrosion, and potential for strength.